In this article it is shown how to generate various important signals in Matlab. The different types of signal includes Unit Impulse, Unit Step, square, rectangle. sawtooth and others. In the study of communication system these signals appear frequently and thus knowledge about how to generate them in Matlab is important. For more see matlab tutorials and matlab software download.
Here we show the generation of following signals-
The dirac delta function (continuous and discrete)is defined as-
\[\delta(t)=\begin{cases}1 & t = 0\\0 & otherwise\end{cases}\]
or,
\[\delta(n)=\begin{cases}1 & n = 0\\0 & otherwise\end{cases}\]
To generate a unit Impulse the following matlab statement can be used-
>> Imp=[1 zeros(1,N-1)]
Let the number of zeros be N=8, then
>> Imp=[1 zeros(1,7)];
This creates a sequence- 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Applying stem function-
>> stem(Imp)
gives the following graph-
To create shifted unit impulse we can use the following matlab statement-
>> Imp_shift= [zeros(1,k-1) 1 zeros(1,N-k)]
If N=8 and k=2,
>> Imp_shift[zeros(1,1) 1 zeros(1,6)]
gives the sequence- 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0
and,
>> stem(Imp_shift)
gives the following graph-
2. Unit Step Function
The unit step function is defined as-
\[u(t)=\begin{cases}1 & t \geq 0\\0 & t < 0\end{cases}\]
or,
\[u(n)=\begin{cases}1 & n \geq 0\\0 & n < 0\end{cases}\]
To generate unit step sequence of length N the following matlab statement can be used-
u_step=[ones(1,N)]
let N=8, then we have
>> u_step=[ones(1,8)]
gives the sequence- 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
>> stem(u_step)
gives the following graph-
Similarly, to generate a shifted unit step sequence u(n-k)we can use the following matlab statement-
u_step_shift=[zeros(1,k) ones(1,N)]
let N=8, k=3 then,
>> u_step_shift=[zeros(1,3) ones(1,8)]
gives the sequence- 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 (that is, three Zeros followed by eight Ones)
>> stem(u_step_shift)
gives the following graph-
Another method to generate unit step function is to use the heaviside(x) matlab function. The following command and graph illustrates generation of unit step function using this heaviside(x) command.
>> n = -5:0.01:5;
>> u_step = heaviside(n);
>> plot(n,u_step)
This gives the following graph-
It's also easier to use heaviside function to generate a shifted unit step u(t-to) (or u(n-k)) as illustrated below-
>> n = -5:0.01:5;
>> u_step_shift = heaviside(n-2);
>> plot(n,u_step_shift)
3. Signum Function
The Signum function is defined as-
\[sign(t)=\begin{cases}1 & t< 0\\0 & t=0\\-1 & t>0\end{cases}\]
or,
\[sign(n)=\begin{cases}1 & n< 0\\0 & n=0\\-1 & n>0\end{cases}\]
To generate the sign(n) function the matlab code is-
>> n=-5:0.01:5;
>> y=sign(n);
>> plot(n,y)
The graph is shown below-
4. Square wave signal
Square signals can be generated using the square(t,duty) function. This function generates a periodic square wave with period T=2*pi with +ve and -ve unity peak value over the range defined by parameter t. The parameter duty defines percentage of period T over which the square wave remains positive.
Example: To generate a square wave over two period 2T=4*pi and amplitude of 2
>> t=0:0.001*pi:4*pi;
>> y=2*square(t);
>> plot(t,y)
The plot is shown below-
5. Rectangular wave signal
To generate rectangular signal in matlab we can use rectpuls(t) or rectpuls(t,w). rectpuls(t) function generates a continuous, aperiodic and unity height rectangular pulses. rectpuls(t,w) is same as rectpuls(t) with additional parameter w which allows to define width of the pulse.
Example:
To generate a rectangular pulse of amplitude 2, pulse width 3 we use the following commands-
>> t=-5:0.01:5;
>> y=2*rectpuls(t,3);
>> plot(t,y)
>> axis([-6 6 -0.5 3]);
The graph generated is shown below-
Here we show the generation of following signals-
- Unit Impulse signal
- Unit Step signal
- Signum signal
- Square wave signal
- Rectangular wave signal
The dirac delta function (continuous and discrete)is defined as-
\[\delta(t)=\begin{cases}1 & t = 0\\0 & otherwise\end{cases}\]
or,
\[\delta(n)=\begin{cases}1 & n = 0\\0 & otherwise\end{cases}\]
To generate a unit Impulse the following matlab statement can be used-
>> Imp=[1 zeros(1,N-1)]
Let the number of zeros be N=8, then
>> Imp=[1 zeros(1,7)];
This creates a sequence- 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Applying stem function-
>> stem(Imp)
gives the following graph-
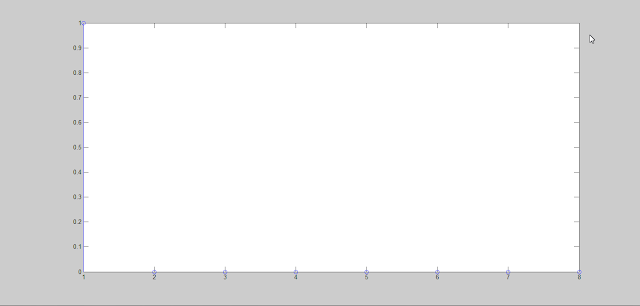 |
| Unit Impluse Sequence |
>> Imp_shift= [zeros(1,k-1) 1 zeros(1,N-k)]
If N=8 and k=2,
>> Imp_shift[zeros(1,1) 1 zeros(1,6)]
gives the sequence- 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0
and,
>> stem(Imp_shift)
gives the following graph-
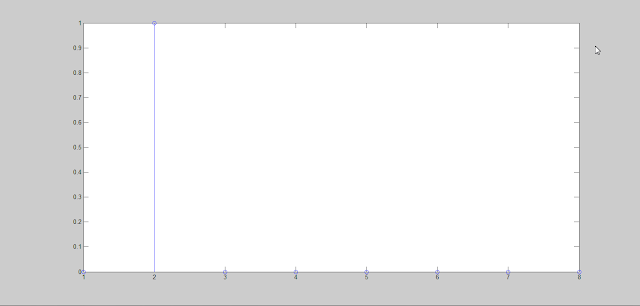 |
| Shifted Unit Impulse |
2. Unit Step Function
The unit step function is defined as-
\[u(t)=\begin{cases}1 & t \geq 0\\0 & t < 0\end{cases}\]
or,
\[u(n)=\begin{cases}1 & n \geq 0\\0 & n < 0\end{cases}\]
To generate unit step sequence of length N the following matlab statement can be used-
u_step=[ones(1,N)]
let N=8, then we have
>> u_step=[ones(1,8)]
gives the sequence- 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
>> stem(u_step)
gives the following graph-
 | ||||
| unit step sequence |
u_step_shift=[zeros(1,k) ones(1,N)]
let N=8, k=3 then,
>> u_step_shift=[zeros(1,3) ones(1,8)]
gives the sequence- 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 (that is, three Zeros followed by eight Ones)
>> stem(u_step_shift)
gives the following graph-
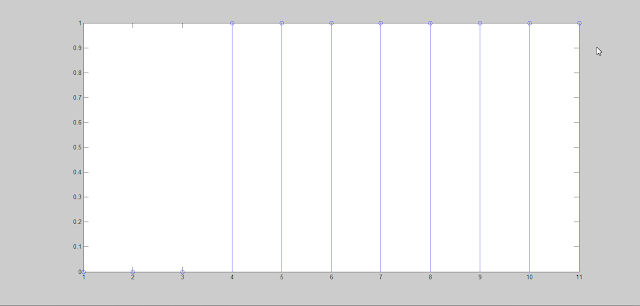 |
| shifted unit step sequence |
Another method to generate unit step function is to use the heaviside(x) matlab function. The following command and graph illustrates generation of unit step function using this heaviside(x) command.
>> n = -5:0.01:5;
>> u_step = heaviside(n);
>> plot(n,u_step)
This gives the following graph-
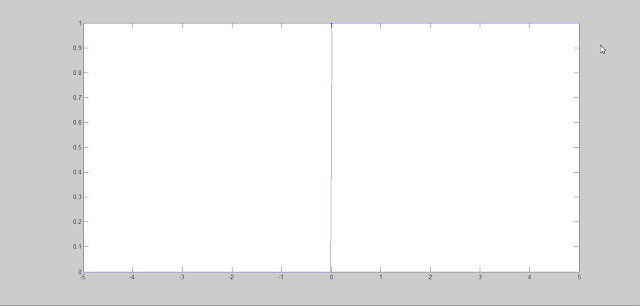 |
| unit step function using heaviside function |
It's also easier to use heaviside function to generate a shifted unit step u(t-to) (or u(n-k)) as illustrated below-
>> n = -5:0.01:5;
>> u_step_shift = heaviside(n-2);
>> plot(n,u_step_shift)
 |
| shifted unit step function using heaviside function |
The Signum function is defined as-
\[sign(t)=\begin{cases}1 & t< 0\\0 & t=0\\-1 & t>0\end{cases}\]
or,
\[sign(n)=\begin{cases}1 & n< 0\\0 & n=0\\-1 & n>0\end{cases}\]
To generate the sign(n) function the matlab code is-
>> n=-5:0.01:5;
>> y=sign(n);
>> plot(n,y)
The graph is shown below-
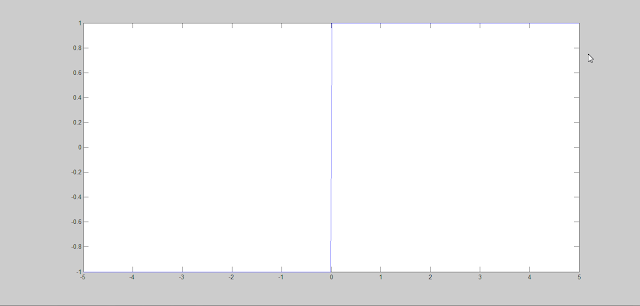 |
| Signum function |
Square signals can be generated using the square(t,duty) function. This function generates a periodic square wave with period T=2*pi with +ve and -ve unity peak value over the range defined by parameter t. The parameter duty defines percentage of period T over which the square wave remains positive.
Example: To generate a square wave over two period 2T=4*pi and amplitude of 2
>> t=0:0.001*pi:4*pi;
>> y=2*square(t);
>> plot(t,y)
The plot is shown below-
 |
| Square wave signal |
To generate rectangular signal in matlab we can use rectpuls(t) or rectpuls(t,w). rectpuls(t) function generates a continuous, aperiodic and unity height rectangular pulses. rectpuls(t,w) is same as rectpuls(t) with additional parameter w which allows to define width of the pulse.
Example:
To generate a rectangular pulse of amplitude 2, pulse width 3 we use the following commands-
>> t=-5:0.01:5;
>> y=2*rectpuls(t,3);
>> plot(t,y)
>> axis([-6 6 -0.5 3]);
The graph generated is shown below-
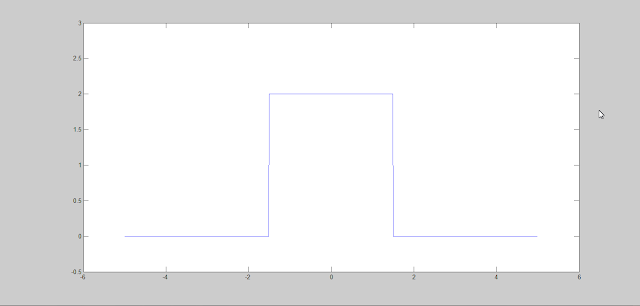 |
| rectangular pulse |
Tidak ada komentar:
Posting Komentar